In today’s world, having control over your reproductive health is essential for effective family planning. With numerous contraception methods available, understanding your options allows you to make informed choices that align with your lifestyle, health needs, and plans. This guide explores various contraception methods, from non-hormonal options to permanent solutions, helping you navigate this important aspect of sexual health.
Understanding Contraception: The Basics
Contraception, commonly called birth control, encompasses various techniques aimed at preventing conception. These approaches function through different mechanisms– blocking sperm-egg interaction, suppressing ovulation, or altering uterine conditions to hinder fertilization. Effectiveness and suitability vary based on health profiles, lifestyle factors, and individual priorities.
Non-Hormonal Birth Control Options

For those who prefer to avoid hormonal methods due to medical conditions, personal choice, or sensitivity to hormones, several effective non-hormonal options exist:
Copper IUD: Long-lasting Protection Without Hormones
Among non-hormonal choices, the copper intrauterine device (IUD) provides the highest level of effectiveness. A healthcare professional inserts this device, which protects against pregnancy for up to 12 years. By releasing copper ions, it creates an environment that stops sperm from reaching the egg and may also prevent fertilization. Some users notice heavier periods or cramping initially, but these often improve within a few months. Boasting over 99% effectiveness, the copper IUD stands out as a top choice for those seeking hormone-free protection that lasts for years.
Also read: Family Planning: A Wise Choice!
Barrier Methods: Physical Prevention
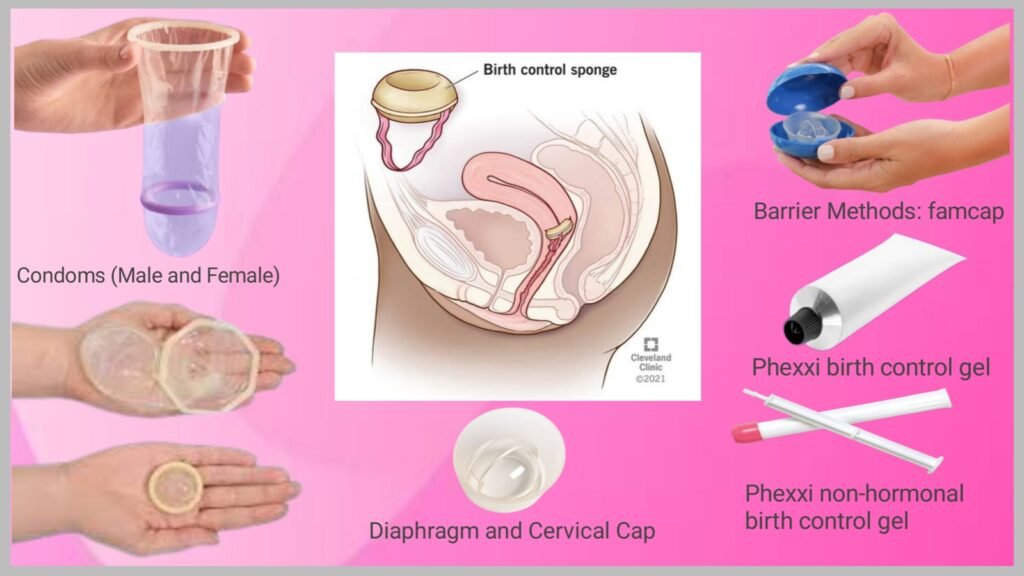
Barrier methods work by stopping sperm from meeting the egg through physical blockage. Popular options include:
1. Condoms (Male and Female): These are the only options that protect against both pregnancy and STIs. Male condoms offer 82% effectiveness with regular use, while female condoms provide approximately 79% protection.
2. Diaphragm and Cervical Cap: These silicone cups cover the cervix and block sperm.When used with spermicide, diaphragms achieve 88% effectiveness when inserted correctly.
3. Contraceptive Sponge: A soft, spermicide-coated disc placed in the vagina to trap and disable sperm.
4. Spermicides and Vaginal Gels: Products like Phexxi gel maintain vaginal acidity to immobilize sperm, offering a hormone-free chemical barrier.
Natural Family Planning Methods
Also known as fertility awareness methods, these approaches involve tracking fertility patterns to avoid intercourse during fertile periods. While requiring diligent tracking and abstinence during fertile windows, these methods appeal to those seeking hormone-free options without devices or chemicals.
Long-Acting Reversible Contraception (LARC)
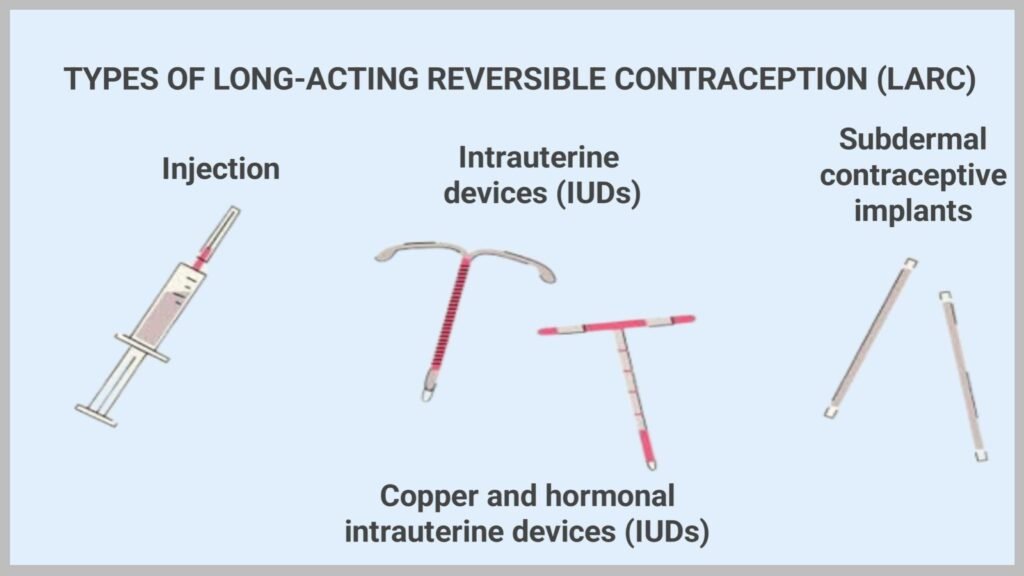
LARC methods offer the advantage of long-term protection without requiring daily, weekly, or monthly attention:
Intrauterine Devices (IUDs)
Hormonal IUDs slowly release progestin into the uterus, offering similar long-term protection as their copper counterparts. Both types have a failure rate below 1%, making them one of the most reliable choices.
Contraceptive Implants
A matchstick-sized rod inserted under the skin of the upper arm steadily releases progestin to prevent pregnancy for up to five years. Like IUDs, implants are over 99% effective and completely reversible—fertility returns quickly after removal.
The primary benefits of LARC methods include:
* “Set it and forget it” convenience
* Extremely high effectiveness (>99%)
* Cost-effectiveness over time
* Quick return to fertility after removal
* Reduced menstrual symptoms for many users (hormonal options)
Emergency Contraception Pills: A Backup Plan

Commonly known as the “morning-after pill,” emergency contraception functions by postponing or stopping ovulation following unprotected sex or contraceptive mishaps. There are two main types:
1. Levonorgestrel-based pills: (Plan B One-Step, Take Action): Available without a prescription, these are most effective when taken within 72 hours of unprotected sex but can work up to 5 days after.
2. Ulipristal acetate pills: (Ella): Available by prescription only, these maintain effectiveness throughout the 5-day window after unprotected sex.
Emergency contraception does not end an existing pregnancy – it prevents pregnancy from occurring. Side effects may include nausea, headache, fatigue, abdominal cramps, and temporary menstrual irregularities, but these typically resolve within a few days.
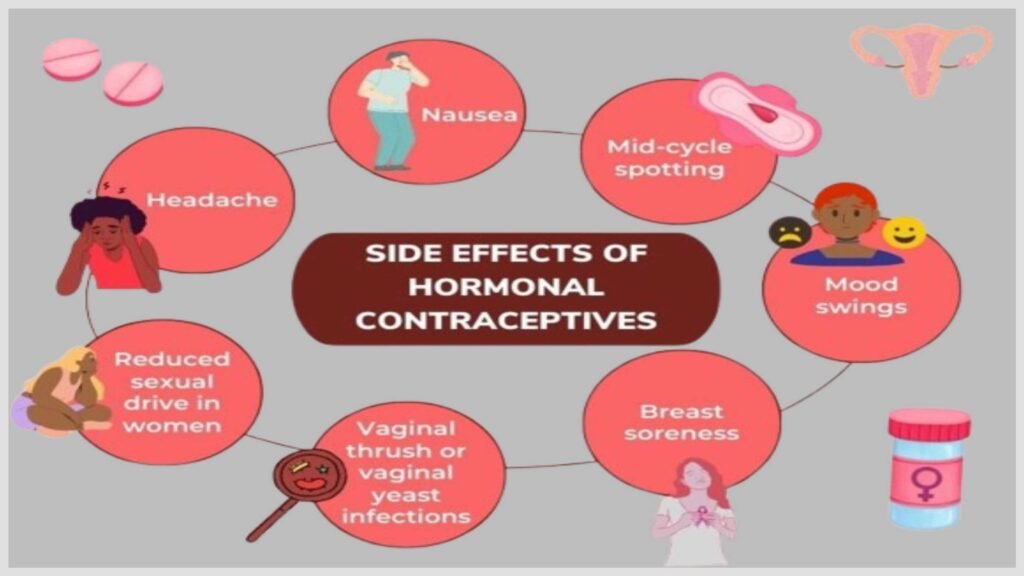
Hormonal Birth Control Side Effects: What to Expect
Hormonal birth control uses two types: some combine estrogen and progestin, while others use only progestin. Common methods include:
* Combined hormonal contraceptives (pills, patches, vaginal rings)
* Progestin-only methods (mini-pills, hormonal IUDs, implants, injections)
While highly effective at preventing pregnancy, hormonal methods may cause side effects, including:
* Headaches
* Nausea
* Mood changes
* Breast tenderness
* Weight fluctuations
* Acne (which may improve or worsen)
* Changes in menstrual patterns
While effective, hormonal methods may cause temporary side effects like headaches, nausea, mood swings, or irregular bleeding. Most side effects typically improve within a few months as your body adapts to the hormonal changes. Serious risks (e.g., blood clots) are rare but should be discussed with a provider.
Barrier Contraception Methods: Simple Protection

Barrier methods function by physically blocking sperm from reaching and fertilizing an egg. These methods offer several advantages:
* No hormones
* Available without prescription (except for fitted diaphragms)
* No long-term side effects
* Protection against STIs (condoms only)
* Immediate return to fertility
However, barrier methods are generally less effective with typical use than hormonal or long-acting reversible options. Using barrier methods consistently and correctly significantly improves their effectiveness, and combining methods (like condoms with spermicide) offers enhanced protection.
Also read: Natural Family Planning: 6 Fertility Secrets
Permanent Contraception Options: When You’re Sure
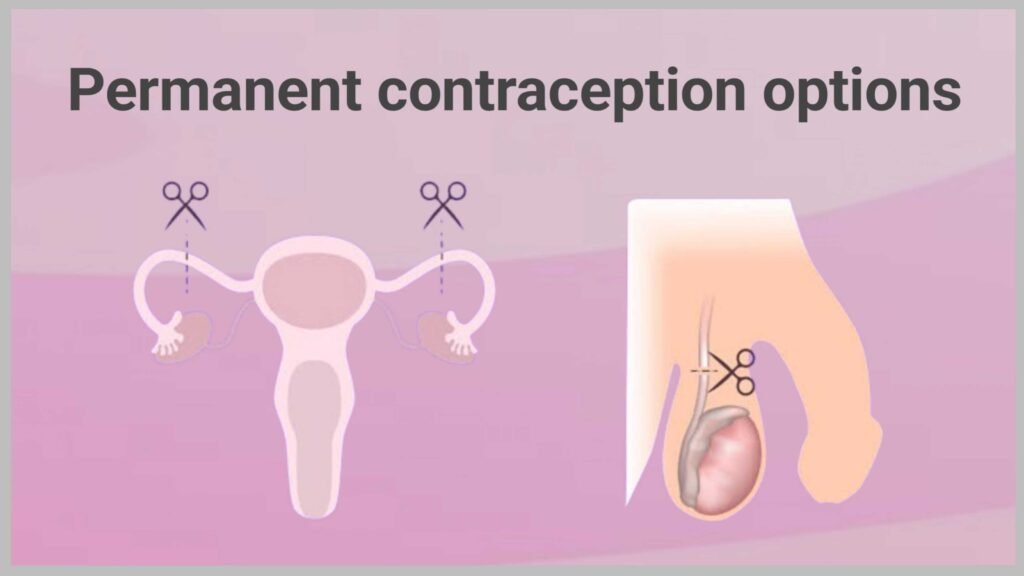
If you’re sure you don’t want kids later, permanent contraception offers a lifelong solution:
Tubal Surgery for Women
Often called “getting your tubes tied,” tubal surgery involves blocking, cutting, or sealing the fallopian tubes to prevent eggs from reaching sperm. Modern approaches include:
* Laparoscopic tubal ligation: A procedure using miniature abdominal incisions for minimally invasive access to fallopian tubes.
* Abdominal approaches: May be performed immediately after childbirth
Tubal surgery has a 0.5% failure rate, making it highly reliable, but it’s designed as a permanent solution.
Vasectomy for Men
A vasectomy is a fast procedure that blocks the tubes carrying sperm. Benefits include:
Typically requires less downtime than female sterilization procedures:
* Minimal downtime (1–2 days)
* Local anesthesia only
* High effectiveness (99.85%) after confirming success via semen tests
* Generally involves less downtime compared to procedures for women
Both permanent methods share important considerations:
* They don’t protect against STIs
* They should be viewed as irreversible
* It’s crucial to discuss the permanent nature and other options with a professional
* They offer immediate (tubal surgery) or confirmed (vasectomy) protection after the procedure
Making Your Choice: Factors to Consider
When selecting a contraception method, several factors come into play:
1. Effectiveness: How critical is avoiding pregnancy for you?
2. Lifestyle: Can you manage daily pills, or is a low-maintenance option better?
3. Hormone Sensitivity: Do you have concerns about hormonal methods?
4. STI Protection: Do you need protection against sexually transmitted infections (STIs)?
5. Future Fertility Plans: When do you want to conceive, if at all?
6. Health Factors: Do you have medical conditions that might affect your options?
7. Personal Preferences: Religious, cultural, or personal values may influence your choice.
Conclusion: The Informed Choice Is Yours
The ideal contraception method fits your lifestyle, health needs, and reproductive goals. Many individuals find their contraceptive needs change throughout their reproductive years, and it’s completely normal to switch methods as your circumstances evolve.
Consulting with a healthcare provider can help you navigate these options, addressing any concerns specific to your health history. Choosing contraception is personal—pick what fits your routine and feels right for you.
Whether you’re looking for non-hormonal alternatives, considering long-term options, or exploring permanent solutions, today’s wide range of contraceptive methods offers more choices than ever before, empowering you to take control of your reproductive health journey.