Introduction to Preconception Health
Preconception health is the health of both women and men of childbearing potential with a focus on the preconceptional time. It is action upon the optimal preconception health in that it is a major determinant of fertility and subsequent pregnancy outcomes. Preconception health is defined as knowledge and management of a collection of risk factors among the physical, genetic, psychosocial, environmental, and behavioral factors that affect pregnancy. They include obesity, diabetes, hypertension, cigarette smoking, drug abuse, and some genetic disorders.
Preconception Nutrition Guide

Good pre-pregnancy diet is important in several ways: it helps prepare your body for conception and in several ways supports early fetal development. Good diet supports fertility and sets the stage for healthy pregnancy.
Nutrients Required for Conception
A balanced diet rich in nutrients can prepare your body for pregnancy and increase fertility. Consume the following nutrients in proper quantities in the first place:
- Folate/Folic Acid: A minimum of 400 micrograms daily will avert neural tube defects. Leafy green vegetables, fortified cereals, and legumes are some examples.
- Iron: Storage of iron before pregnancy prevents anemia. Supplement your iron stores with foods rich in nutrients such as grass-fed beef, lentils, and kale.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: The healthy fats assist in the development of the embryo. Take marine sources like salmon, chia seeds, and algae-based supplements before anything else.
- Antioxidants: Vitamins C, E, and selenium shield cells from harm. Nuts, vegetables, and fruit are a good source.
Slow-Release Carbohydrates: Choose slow-release carbohydrate foods like oatmeal, barley, and whole-grain bread that level out insulin and reproductive hormones.
Food to Use and Avoid
Preconception diet planning involves both inclusion and exclusion of food. A meal consisting of a fruit, a vegetable, whole grain, lean meat, and milk should provide you with the necessary diet of all the nutrients. The healthiest pregnancy food is the healthiest food for overall well-being as well, with the inclusion of whole grains, good fats, and proteins.
Foods that should be avoided or limited during this time are:
- Swordfish and king mackerel with high mercury levels
- Excessive caffeine (up to 200mg daily)
- Packaged foods and alcoholic beverages
- Trans fats in the majority of packaged foods
- Synthetic preservative and additive with ingredients
Male Fertility Optimization

Preconception health only refers to women. Men’s health and men’s reproductive health are also critical to conception and pregnancy outcome. Male fertility optimization needs to be incorporated into any preconception health plan.
Lifestyle Factors Affecting Male Fertility
Several lifestyle factors directly influence sperm count and quantity:
- Temperature Control: Production is increased with lower temperatures. Wear cotton underclothes and don’t sit on hot computer or laptop chairs for long periods.
- Exercise: Routine exercise such as exercise cycling or running to increase blood flow and sperm viability.
- Weight Management: Healthy weight maintains the balance of hormones—obesity can augment release of estrogen but underweight can inhibit testosterone, both of which are not healthy for the quality of the sperm.
- Minimizing Stress: Stress, especially chronic stress, changes the level of cortisol, which can affect the health of sperm. Try research methods such as nature therapy or controlled breathing to assist in reducing stress.
Nutrients for Sperm Health
Some nutrients enable optimal sperm performance and production:
- Zinc: Nuts and seeds that are rich in zinc such as oysters (which are zinc-rich per serving), roasted pumpkin seeds, and dark chocolate (70% and above cocoa) aid testosterone development and sperm membrane stability.
- Selenium: Sunflower seeds, turkey breast, and pasture eggs supply bioavailable selenium to protect sperm DNA from oxidative stress.
- Vitamin C: Prevents sperm agglutination and enhances motility. Have a serving of papaya, kiwi, or red peppers as your vitamin C.
- Coenzyme Q10: Maintains mitochondrial function in sperm. Suggest supplements or incorporate sardines and peanuts into foods.
- L-carnitine: Enhances sperm motility. Present in red meat, poultry, and milk.
Prenatal Vitamin Suggestions
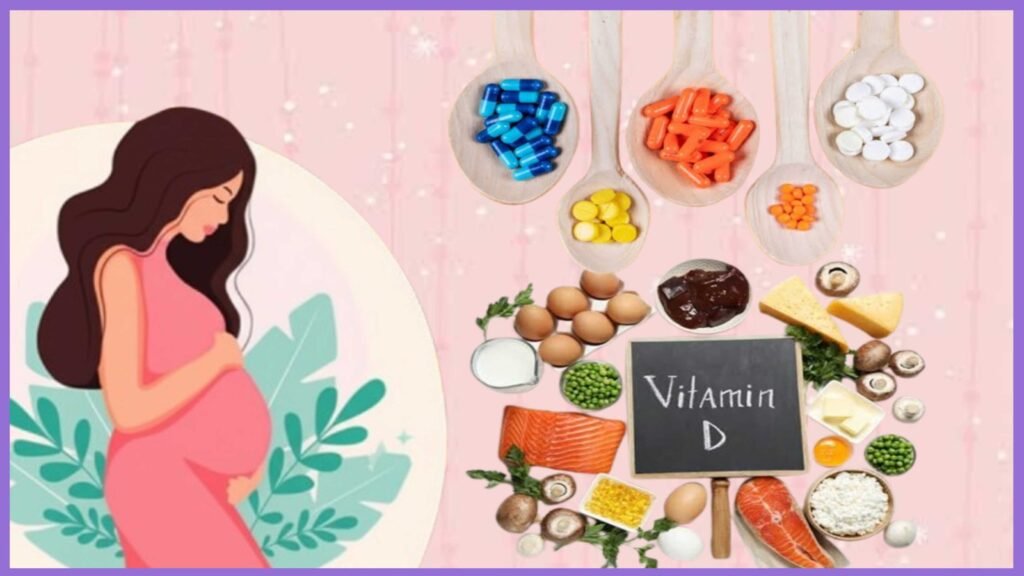

Taking prenatals before you get pregnant ensures that your body is at the optimal levels of nutrition during pregnancy. Good-quality supplements are nutritional insurance, filling in the gaps that even the best diet can’t.
Prenatal Vitamin Key Ingredients
When choosing a prenatal vitamin, search for these essential ingredients:
- Folic Acid/Folate: 400-800 mcg daily, in the form of methylfolate if possible
- Iron: 27 mg to prevent anemia and maintain greater blood volume
- Calcium: 1,000 mg to aid in bone and tooth development
- Vitamin D: 600 IU for calcium absorption
DHA: Supplement with omega-3 rich foods like algal oil to enhance fetal brain development..
Iodine: Take 150 mcg per day in kelp tablets or iodized salt to keep metabolism in balance.. - Choline: Take 450 mg from egg or supplement for brain structure formation.
When to Take Prenatal Vitamins
Begin three months before conception to build up reserves of nutrients, in this case, folate, that will be needed when the embryo is in the phase of active cell division. Throughout your pregnancy, the recommendation is to begin taking a daily prenatal supplement as soon as possible, and at least for the first 12 weeks of pregnancy when organs of the fetus begin to form.
Fertility-Enhancing Lifestyle Modifications

Aside from supplements and diet, lifestyle changes can also make their impact felt on fertility. Practicing them at the earliest possible stage creates a favorable environment for conception and pregnancy.
Exercise and Weight Control
Healthy weight with considered movement and regulated portions maximizes reproductive potential:
- Strive for approximately 2.5 hours of moderate physical activity per week, like brisk walking or swimming.
- Emphasize strength training, walking, swimming, or yoga
- Steer clear of high or high-intensity exercise that could disturb hormonal balance
- Work with health care providers to attain a BMI of 18.5-24.9
Stress Management Skills
Stress negatively impacts fertility in both men and women by disrupting the release of hormones:
- Daily mindfulness meditation practice
- Try doing gentle yoga specific to fertility
- Apply cognitive behavior therapy for depression or anxiety
- Build healthy friendships or support groups to serve as a stress buffer.
- Sleep well (7-9 hours at night)
Environmental Toxins to Avoid
Reducing exposure to environmental pollutants can increase fertility success:
- Limit plastic food packaging and never microwave plastic-covered food
- Opt for pesticide-free fruits and vegetables whenever available, focusing on the Environmental Working Group’s “Clean Fifteen” produce.
- Conduct practice in the use of natural chemical-free cleaning products
- Avoid tobacco smoke, including secondhand exposure
Preconception Genetic Screening
Pre-pregnancy genetic testing may uncover risks and allow you to make the right choices. Knowing your genetics allows you and your doctor to make the right preconception and prenatal care decisions.
Preconception Genetic Tests Types
There are a number of screening tests:
- Carrier Screening: Genetic screening for genetic diseases including cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, and Tay-Sachs disease
- Chromosomal Analysis: Identifies structural chromosome abnormalities
- Comprehensive Carrier Screening: Tests for several hundred genetic disease conditions at once
- Whole Exome Sequencing: More advanced testing that scans gene sequences for unusual mutations, usually used when preliminary screenings do not work.
Who Should Undergo Genetic Screening
While available to everyone, preconception genetic screening can be particularly beneficial to some people:
- With inherited disorders prevalent in their family
- Patients from some ethnic groups having higher rates of some genetic disorders
- Pregnant women aged more than 35 years
- People with a history of recurrent pregnancy loss
- Established genetic mutation patients
Preconception counseling would entail consideration of a patient’s history, family history, etc., to determine what types of tests would be indicated. Pre- or post-test genetic counseling counsels couples about results and aids in decision-making.
Preparing Body for Pregnancy
Physical preparation for pregnancy is a comprehensive healthcare routine starting months before getting pregnant. Such routines prepare your body to conceive and deliver a healthy baby.
Preconception Medical Screening
Arrange for a full preconception checkup with your health care provider in order to:
- Review your history of previous illness and medications
- Get necessary immunizations (namely rubella and varicella)
- Test for infections that may affect pregnancy
- Collaborate with specialists to optimize control of conditions such as risks of gestational diabetes, hypertensive disorders, or hypothyroidism before pregnancy.
- Document any previous pregnancy complications
Dental Health
Notably, oral healthcare impacts pregnancy complications:
- Get a dental checkup and cleaning prior to pregnancy
- Treat any gum disease, which has been linked to preterm birth
- Complete any mandatory dental work before pregnancy
- Cultivate good oral hygiene practice
Mental Health Preparation
Mental health is an important preconception health:
- Treat existing mental illness with counseling
- Learn how to cope with pregnancy stressors
- Build a mental health professional, family, and peer support network to manage emotional concerns at the preconception stage.
- Investigate specialty counseling sessions in fertility and prenatal planning
- Evaluate work-life balance and any adjustments needed while pregnant Conclusion
Conclusion
Preconception health is a holistic approach to preparing your body for pregnancy. From diet and vitamin intake to lifestyle modification and medical testing, taking charge in your own hands before conception can affect pregnancy and fertility. Women and men should both participate in preconception health habits since women and men both have a stake in pregnancy and fertility health. By adhering to the guidelines provided in this article, you’ll be making serious strides toward maximizing your preconception health and paving the way for healthy pregnancy.
Remember that preconception health is very individualized, and you will have to work with medical professionals in order to develop a plan that will be specific to your own needs and situation. Start making these modifications three to six months before conception for maximum impact, but also remember that any positive changes will have positive consequences.